The Move to Digital
Since the invention of microchips and semiconductor transistors in the 1950’s, the world has moved steadily to more and more digital information. Computers for government, then computers for business, then home computers brought vast amounts of data into digital formats, and with the birth of the World Wide Web digital information has exploded in volume.
Today, we rely on digital documents for our business operations, our finances, our government, our healthcare, our legal system, and vast amounts of news and information—both personal and public. Trusting such digital documents is critical to ascertaining truth and accurately conveying facts.
“Documents comprise evidence, and are generally assumed to amount to evidence upon which the parties and the court can rely,” explains Helen Brander for Counsel magazine. “For every point that is made, one hopes there is a document to support that point.”
The Risk of Fraud
Throughout history, there have been various techniques to authenticate documents. In the pre-industrial age, it was common in Europe for someone to sign a document in ink and to then press a wax seal on the document to indicate the authenticity of that document. It was always possible, of course, that someone could tamper with the document and forge signatures, information, or the wax seal itself.
In the modern age, the United States has notary publics who can witness a person signing a document and endeavor to authenticate the signer’s identity by inspecting a driver’s license, passport, or other form of identification for that person. Again, the risk remains that it is possible to forge such identity materials, or alter the actual documents or signatures after signing.
More recently, with the popularity of electronic or digital documents, the digitization of business processes is taking place. In other words, from the creation of documents, to the signing of documents, to the storage and subsequent retrieval of documents, one or more steps may be conducted digitally.
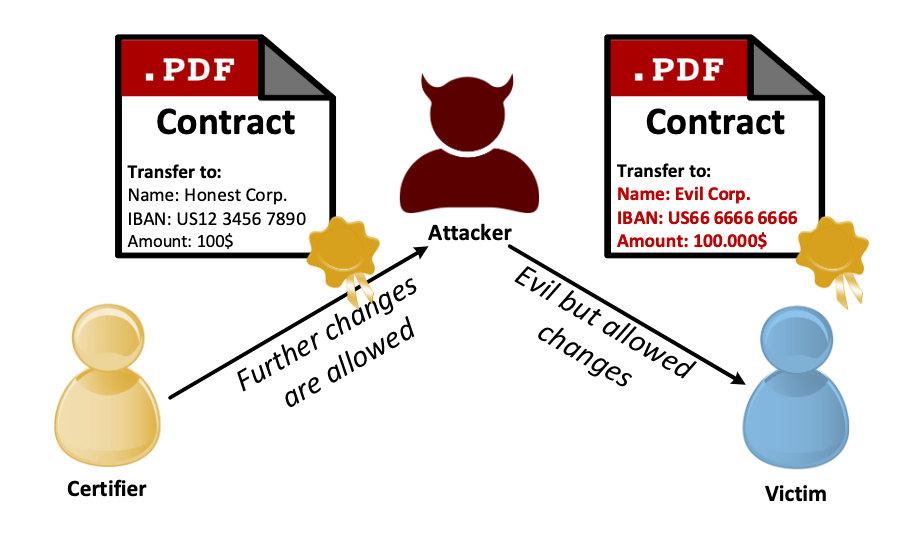
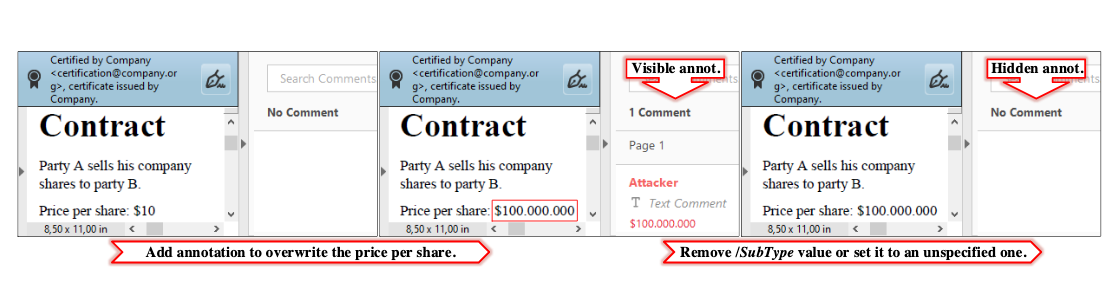
For example, a document may be created on a computer and subsequently printed, signed with wet ink or electronically, then faxed, delivered via courier, or scanned into the computer and finally shared electronically via email or by using other file transfer mechanisms. Despite the technology advances, such documents can still be tampered with and signatures can be forged within this process as well.
“Detecting fraud within documents that have been digitally altered with graphics editors or ‘print-manipulate-scan’ evasion techniques requires more sophistication,” notes Martin Rehak in a Help Net Security article. “Often undetectable to human fraud specialists, building an automated solution requires specialist knowledge of the metadata and digital footprints left by scanning and printing devices.”

As such, modern digital documents require a level of security as evolved and nuanced as the technologies producing, storing, and sharing the digital documents themselves.
The Security of ZorroSign
Facing this historical need, ZorroSign has developed a unique digital solution that can:
- Prove that the individual who is performing the action to sign the document is who they claim to be (verification);
- Apply a digital equivalent of a wet-ink signature to the document (legal intent); and,
- Prove the authenticity of the printed copy or digital version of an electronically signed document, its content, attachments, and the signatures on it (authenticity).

ZorroSign’s patented Z-Forensics token is a tamper and fraud-detection seal for your digital documents, creating an unprecedented, immutable audit trail and complete chain-of-custody validation.
This revolutionary security system allows a validated user to create an electronic document, then allow one or more other users to complete and sign that document in a particular sequence—”the workflow”—all the while capturing the chain of custody and an audit trail of the changes made to the document by the parties in the workflow, such as recording key authentication, security and validation information when an action took place.
Unlike any other digital signature solution, ZorroSign seals all documents with our Z-Forensics token—capturing the complete audit trail and accompanying attachments and signature workflow. The token is encrypted and contains all the details about the transaction: Time stamps, user authentication, documents and attachments.
Only the Z-Forensics token:
- Allows ZorroSign customers to manage permissions as to who gets to see what level of information about the transaction and the contract
- Stores the ZorroSign security encryption certificates, which—unlike other digital security certificates—never expire
- Can verify, validate and authenticate both digital and printed (paper) version of electronically signed contracts
Our Z-Forensics feature enables ZorroSign users to create a virtual seal for every uploaded document: initiating a verifiable trail, tracking every step of a document’s journey through users, so that any attempts at tampering, fraud, revision or other alterations are immediately captured.
To learn more about Z-Forensics and how ZorroSign can help you prevent fraud with digital documents, contact us today!