- Published on
Digital Transformation: Securing Transactions and Ensuring the Chain-of-Custody
- Authors
-
-
- Name
- Michael Jones
-
The digitization of information has its roots in the 1950’s and the progression of both technology and society has been blurringly fast the past 70 years.

Individuals, businesses, organizations, and even governments are moving to digital operations at an incredible pace.
Today, faster and faster chips . . .
Run on smaller and smaller devices . . .
Coupled with faster and faster networks . . .
Able to deliver greater amounts of data (even VR and AR) . . .
To a greater number of devices!
The digitization of the real world has even inspired plans for entirely digital worlds such as the metaverse!
Moving to digital operations is not only cost-effective for private and public-sector organizations, but has become a necessity in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Digital transformation is no longer an option, but an imperative. Recent research from Accenture has found that in the three years prior to 2018, firms who led their industry in enterprise technology adoption grew two times faster than laggards. Today, they are growing five times faster. The risk is no longer merely getting left behind, but being eliminated altogether.”
~Harvard Business Review
(November 30, 2021)
This need is serviced by a huge range of new technologies for digitization: Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure; communication tools like Monday, Slack, and Zoom; databases like Microsoft and Oracle or blockchain; office tools like Google Docs and Microsoft 360; plus cybersecurity, MSSPs, wireless providers, and all the accompanying hardware and software that produces, stores, and moves digital information.
Securing Transactions with Digital Signatures
To transact business, commerce, government, or individual trade in such a digital ecosystem also requires legally enforceable digital signatures to prove agreement and intent. There are exciting new technologies supporting digital signatures, but how can such solutions provide legal enforceability?
- They must ensure WHO is signing the legal documents via user authentication,
- They must ensure WHAT was signed (agreed upon) via immutable document control with full audit trail of changes for document verification, and
- They must ensure WHERE, WHEN, and HOW digital signatures were executed in signing ceremonies via metadata captured on digital devices and digital network.
On June 30, 2000, then President Bill Clinton signed the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (E-Sign Act), establishing that electronic signatures have the same legality as traditional signatures on paper, and defined the criteria for legality. The legislation opened the door for digital transactions and digital commerce boomed in its wake.
Digital Signatures on Blockchain
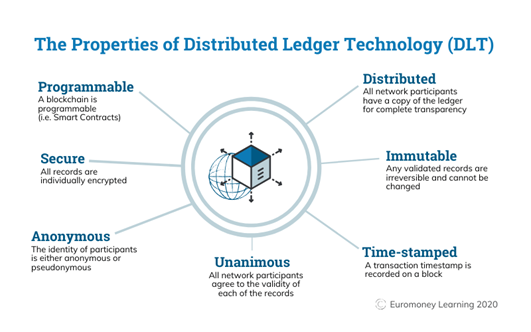
Since 2000, several technologies have come to market to deliver digital signatures, but when a distributed ledger technology—such as blockchain—is used for digital signatures, signers gain the unique advantages of:
- Privacy — with a private blockchain, only participants to the transaction can see details of the transaction, and those participants share equal access to such details
- Immutability — all records and changes are tracked and cannot be changed, providing important chain-of-custody audit capabilities for courts
- Security — all records are individually encrypted and distributed for better protected from phishing and ransomware attacks
ZorroSign was built from the ground up on Hyperledger Fabric to deliver digital signatures with the superior privacy and security of blockchain. We recently announced a partnership with Provence Blockchain to add that technology to our architecture as well, effectively becoming a multi-chain blockchain platform.
Further, solutions that incorporate Identity-as-a-Service (IDaaS) can authenticate users across multiple dimensions, such as what you know (your login password), what you have (your laptop or mobile device), and who you are (biometrics such as fingerprints or eye iris on the device securing who can access it), etc.
Again ZorroSign, for example, delivers IDaaS via:
- Multi-factor authentication
- Leveraging the biometric capabilities of hardware endpoints to verify user identities
- Adopting password-less logins
- Using dynamic knowledge-based authentication (KBA) features, requiring the knowledge of private information of the individual to prove that the person providing identity information is the actual person
Blockchain and the Digital Chain of Custody
Together, digital signature technologies and blockchain technologies can uniquely ensure the chain-of-custody for digital transactions.
To learn more about how ZorroSign helps governments, organizations, businesses, and individuals move to digital operations—with superior privacy and security—contact us today!