- Published on
Passwordless Future and its Importance to Cybersecurity
- Authors
-
-
- Name
- Michael Jones
-
For most organizations, apps, programs and systems, using a username and password is how they authenticate users, identity and access management (IAM). This protocol often leads people to use passwords that are simple. When passwords get complicated users forget them. As a result, people use the same password or copy and paste passwords. This leads to cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Passwordless environments provide total security without users having to remember complex passwords.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) used to be a premier option only offered by organizations highly focused on cybersecurity. Recently this has changed, and more organizations are utilizing MFA within their login protocols. MFA is increasingly becoming a requirement for small, midsize and large organizations, regardless of the industry.
A new methodology incorporating MFA being implemented by IT Leaders is called Passwordless login and authentication, which eliminates potential cybersecurity vulnerabilities. By using this new methodology to login to applications and systems, users can be validated and authenticated in a more secure manner. With software solutions like electronic and digital signature programs, passwordless login allows users not only to sign electronic documents more efficiently and securely while maintaining complete privacy but also have the highest level of confidence that the intended party is the actual party that is executing the document.
According to Verizon’s 2019 Data Breach report, 80% of data breaches are the direct result of compromised or reused passwords. What’s even more astonishing is Lastpass reports in its 3rd Annual Global Password Security Report that 59% of seasoned IT professionals agree that strengthening user authentication is necessary in order to identify their identity capabilities.
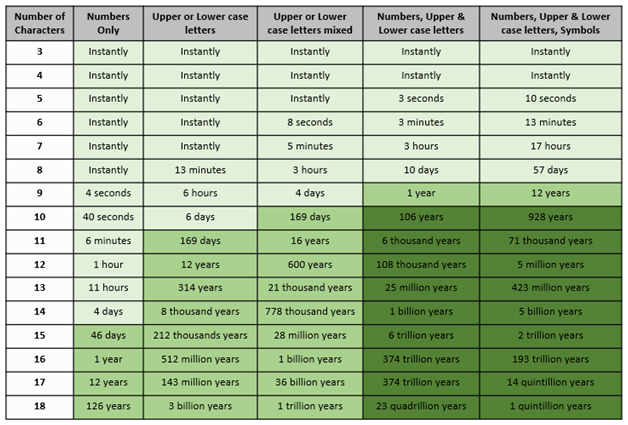
Often when password complexity increases, users are more likely to reuse a password. When passwords are reused security risks increase. Ever wonder just how easy it is for someone with ill intent to crack your password using a computer program? The following table demonstrates the correlation between password strength and the potential time it can take to crack using a specialized computer program.
What is Passwordless login?
Passwordless login incorporating multi-factor authentication is a process in which two or more factors are used to verify a user. A passwordless login is an authentication system that uses alternatives to a password to permit the right users’ access to their account. Popular web-based email systems like Gmail use passwordless logins and users can confirm intent to login via a message on their mobile device, thus controlling access to the account.
For those wondering if multi-factor authentication and two-factor authentication are the same thing, they are not. While they are related, two-factor authentication often secures a user’s account using two separate factors like a password and a separate device pin. While two-factor authentication seems like you are using two separate means to authenticate an account, in actuality a single factor is being used, thus making two-factor authentication and multi-factor authentication different. One-Time Password (OTP) functionality is an example of two-factor authentication. Physical security key, Knowledge Based Authentication and biometrics are examples of MFA.
A physical security key is another way passwordless login can be achieved. To complete login with a physical USB security key a user would plug in the token device into their computer. The service would then authenticate the user and validate account access. Knowledge Based Authentication authenticates users by asking secret questions that only the intended user would have the correct answers. Biometric login is when a system uses biometric login procedures to authenticate a user and provide appropriate access using a device with biometric capabilities. Examples of biometrics is using Apple’s Face ID or the fingerprint scanner on an Android or Apple mobile device.
One MFA method gaining popularity is the use of QR codes. Once the QR code is scanned the mobile device prompts the user for biometric verification. If the device doesn’t have biometric capability the user would receive a pin code via email or text. When authenticated the user would be logged in automatically, achieving a passwordless environment for increased cybersecurity.
Why Governments should adopt Passwordless login as the gold standard
Governments should go passwordless and MFA should be the minimum standard because it is more secure. While many agencies currently use Common Access Cards (CAC) or Personal Identity Verification (PIV) cards to authenticate users, these login protocols are useless on mobile devices and sometimes even cloud based applications. With more applications utilizing the cloud and an increase in users relying on their mobile devices it’s easy to see why CAC and PIV cards need a refresh. Another issue with legacy passwordless protocols in many government agencies is the use of dated Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). Technology drastically changes on average about every six months, this is problematic when you think that the average agency PKI stack is at least 15 years old.
Identity as a Service (IDaaS)
Identity as a Service (IDaaS) is an additional security protocol that corporations and governments can adopt to further secure their systems. An example of IDaaS is the use of Knowledge Based Authentication (KBA) in order to validate a user.
Identity as a Service (IDaaS) will have a major impact on how governments and companies verify users in the future. Advancements in technology, specifically in the space of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) show promise in the ability to use ML in areas like identification, facial recognition and to recognize a true signature on a digitally signed document.
Launch your organization’s passwordless future
The bottom line is that government agencies and the private sector will have to start adopting new technologies to not just keep up with technological advances, but to ensure cybersecurity of their systems and data. It’s important to the public sector and private sector alike to be cyber savvy and have a plan in place to adopt the latest cutting-edge MFA technologies and protocols. For anyone looking for clear benefits of being ahead of the passwordless future, remember that using a passwordless protocol allows an organization to eliminate passwords, which can be a vulnerable access point, while maintaining total control of an organizations access points. Passwordless protocols also increase efficiency by eliminating time spent remembering and recovering lost passwords.
Click here to get in touch with us. You can also email us at [email protected]